Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Diabetes mellitus (DM), commonly referred to as diabetes, is a group of metabolic diseases in which there are high blood sugar levels over a prolonged period.
What causes it?
Diabetes mellitus has multiple possible causes.

First, a quick review of the ways that glucose gets into your cells: while you're resting, insulin lowers blood sugar by causing muscle and fat cells to take up glucose from the bloodstream. The muscle cells use it for energy while the fat cells store it as glycogen until it is needed. When you eat something sweet or starchy, the food raises blood sugar very rapidly because these types of foods break down rapidly into simple sugars in your mouth and small intestine, before being absorbed into your bloodstream. In response to this rise in glucose concentration, beta-cells in your pancreas release more insulin into your bloodstream.
What is Diabetes type 2?
Diabetes type 2 is a chronic condition in which the body does not use insulin properly.
What causes it? The pancreas may not produce enough insulin, or the body may not be able to use the insulin it produces effectively.
What are the symptoms of diabetes type 2, and what can you do to prevent this disease from developing.
The most common symptoms of diabetes type 2 are
polyuria (frequent urination),
polydipsia (increased thirst),
and unexplained weight loss.
Type 2 diabetes is most common in adults, but it's also becoming more common in children and teens. There are many ways to prevent and manage diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes occurs when there are factors like obesity, lack of exercise, and genetics that prevent the body from using insulin correctly.
If someone has diabetes type 2, their pancreas may not produce enough insulin or their cells may become resistant to the hormone, preventing them from getting the energy they need. In this case, insulin injections would be necessary to help regulate blood sugar levels.
What is Diabetes type 1?
Diabetes type 1 is an autoimmune disease in which the pancreas stops producing insulin. This form of diabetes typically develops in children and young adults and requires lifelong treatment with insulin. Without insulin, the body cannot use glucose (sugar) for energy, leading to high blood sugar levels and other serious health problems.
Type 1 diabetes occurs when autoimmune reactions destroy cells in the pancreas that produce insulin.
The main symptoms of diabetes type 1 are excessive thirst and urination, fatigue, weight loss, and blurry vision. In severe cases, high blood sugar levels can cause seizures, coma, or death.
What is the Glycemic Index?
The glycemic index, or GI, is a measure of how quickly a food’s carbohydrates are digested and enter the bloodstream. Carbohydrates that break down quickly have a high GI, while those that break down slowly have a low GI.
What does the glycemic index tell us?
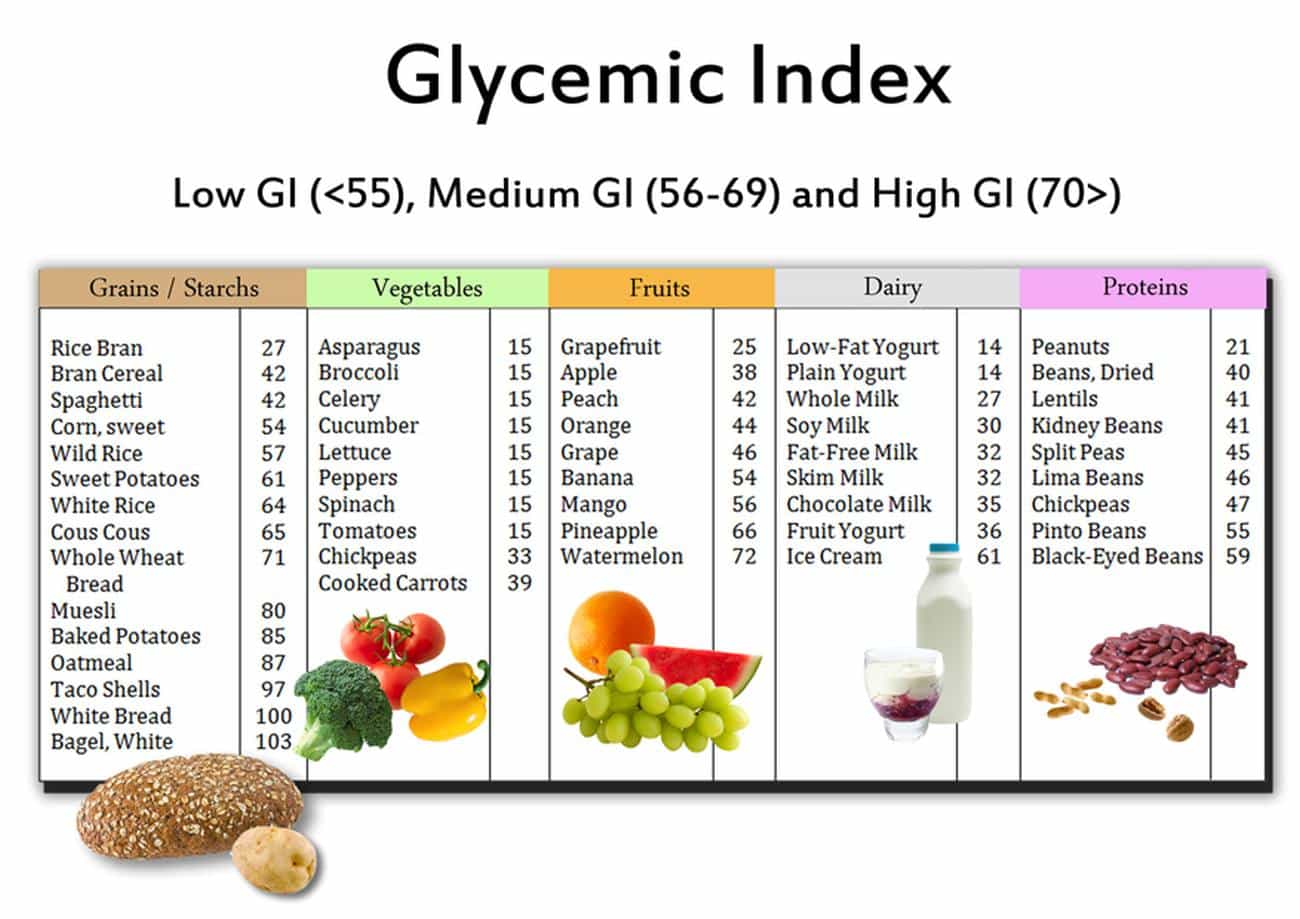
A glycemic index is a valuable tool for understanding how different foods affect blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar, while those with a low GI provide a more gradual rise in blood sugar. This is important for people with diabetes because it can help them to manage their blood sugar levels.
But the glycemic index isn’t just for people with diabetes. It can be useful for anyone who wants to eat healthy, balanced meals. For example, if you’re trying to lose weight, choosing foods with a low GI can help you to keep your blood sugar levels stable and avoid cravings.
HIGH sugar levels
When the blood sugar levels are too high, a person may experience the following symptoms:
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst
- Extreme hunger
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue
If you have diabetes type 2, your body doesn't make or use insulin very well. This is called insulin resistance. So even if your blood sugar levels are high, your cells may not get the message to take in glucose. As a result, your blood sugar levels continue to rise and can damage your organs over time.
LOW sugar levels
What are some common symptoms of low blood sugar levels?
Low blood sugar levels can cause a range of symptoms, including
- shakiness
- dizziness
- sweating, nausea, and
- blurred vision
- In severe cases, low blood sugar levels can lead to seizures or loss of consciousness.
Diabetes, without symptoms
However, some people with diabetes type 2 do not have any symptoms. What can you do to prevent this disease from developing?
You can reduce your risk of diabetes type 2 by maintaining a healthy weight, getting regular exercise, and eating a healthy diet.

Can I reverse diabetes?
There is no one right answer to the question “Can I reverse diabetes?” What works for one person might not work for another. If you have type 2 diabetes, talk to your doctor about what treatment options may be best for you. Treatment options may include medicines, diet, and exercise—or insulin shots if needed. It’s important to work closely with your doctor to find the best treatment plan for you.

If you have questions about reversing diabetes, be sure to talk to your doctor or another health care professional. They can help answer your questions and provide support. You can also find helpful information on the American Diabetes Association website: http://www.diabetes.org/.
The goal of treatment for type 2 diabetes is to keep blood sugar levels as close to normal as possible. This may help prevent or delay complications such as heart disease, stroke, eye problems, kidney problems, and nerve damage. Treatment for type 2 diabetes includes medicines, diet, and exercise.
Insulin
Insulin is a hormone that is produced by the pancreas and helps to regulate glucose in the body so it doesn't get too high or low. Diabetes occurs when there is a problem with insulin production or if the body cannot use insulin properly which causes high blood sugar levels. The more insulin is released, the more glucose your cells will take in. This brings blood sugar levels back down to normal.

Sometimes people with type 2 diabetes need to take insulin shots to help their bodies use glucose for energy. Insulin shots help the body turn sugar into energy. They work by lowering blood sugar levels. You can take insulin shots with a syringe, pen, or pump. If your AIC numbers get close to normal levels, you might be told to switch to pills instead of taking shots.
If you have type 2 diabetes and are taking insulin shots, it’s important to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly. This will help you find the right dose of insulin and keep your blood sugar levels in a healthy range.
There are many different types of blood monitors in the market available today. Ones that require a drop of blood, others that do not require blood.
There are many different types of insulin medication and they all work a little differently. Some insulin medications will start working right away while others take a little longer to get into your system. It's important that you work with your healthcare team to find out which type of insulin is best for you and how often you should be taking it.
By following your doctor's instructions and monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly, you can manage diabetes type 2 and live a healthy, active life
A1C test.
Along with the glucose numbers, there are the A1C numbers.

The A1C assay measures the percentage of all red blood cells that have glucose attached. this number provides a picture of what your blood glucose levels have been like over the last few months and gives your doctor information about your long-term diabetic control (also called glycemic control). For more information on A1C, click here.
PANCREAS
The pancreas is located in the upper abdomen, behind the stomach. It is about six inches long and shaped like a thin, elongated pear.
The pancreas has two main functions: to produce digestive enzymes that help break down food and to produce insulin and other hormones that help control blood sugar levels.
How does diabetes affect the eyes?
Diabetes can affect your eyes in a few different ways, although the effects are usually not permanent. One of the most common eye disorders associated with diabetes is known as diabetic retinopathy.

This disorder is caused by damage to the retina, which is the part of the eye that reacts to light and sends images to the brain via nerve impulses. The retina processes all incoming images, which are then sent to the brain for interpretation. If this process is disrupted, blurred vision will usually result.
How do I know if I have diabetes?
One way of knowing if you have diabetes type 2 is having high fasting blood glucose levels. This means that your blood glucose level at the beginning of the day, before eating anything, is greater than 100 mg/dL after two hours of being measured. Another way is experiencing extreme thirstiness combined with frequent urination. In both cases, this could be a sign that your body isn't using insulin properly which would indicate someone has type 2 diabetes.
In general, blood sugar levels can be lowered with insulin injections and oral medications like metformin, sulfonylureas, and thiazolidinediones. What's important is to work closely with your healthcare team to figure out which medication regimen is best for you.
The Diabetes prognosis
The prognosis for people with diabetes depends on how well they monitor their blood sugar levels and follow the treatment that is prescribed for them. If a person catches type 2 diabetes early and makes changes to their lifestyle, they can prevent serious health problems from developing.
By following your doctor's instructions and monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly, you can manage diabetes type 2 and live a healthy, active life. Thanks for reading!
Sources:
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/in-depth/type-2-diabetes/art-20044784?pg=2










Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.